As the 2010 ended we learned that it was the most prolific years in terms of malware, new malware and botnets. And also we found out that internet browsing has been the most used vehicle to spread infection and attack.
Actually seems not to be an astonishing news, ou contraire, but it is interesting to notice that the focus has shifted from OS related threats to application and browsing vulnerability. this allowed malware to attack new surfaces, virtually any operating systems with internet browsing capabilities is subject and can be target of an attack or an infection: pc, smarthphone, tablet, consoles and any other device.
So let’s try to focus on how this is possible.
The first step is clearly try to understand how browsing works.

When we plan to go to the internet we usually start an application we call browser. to say the truth there are many different kind of browsers, and some does not even looks like a browser.
A browser is, basically, a client that is able to show us the result of a complex HTTP transaction. This kind of capability is used in internet browsers like Internet Explorer, Chrome, Opera, Firefox, Safari running on different platforms (PC, Mac, Pad, smarthphone and so on) but also on email clients (more than 90% of e-mail are actually HTTP documents) as well as games and other program interfaces.
Usually a program that use a browsing capability can refer to a specific (or limited set) of addresses or sources of information, or can point to any allowed resource just typing a web address.

This is the typical activity performed when the user needs to browser the internet using a web browser.
The task start typing the address we want to reach.
when we type something like www.myusualsite.com a lot of things happen in the background.
The first problem is that the browser need to translate the address into an IP address in order to be able to reach the needed resources.
This step is performed using a service called DNS.
A DNS resolution is a complex task that requires some effort. Basically the browser ask to the guest operating Systems to translate the web address
URL into something easier to manage, an IP address.
The Operating Systems query an
Internet server, called DNS, that need to translate the URL into an IP address.
The
DNS server looks into its database to search the address. Since it is not possible for a single DNS server to host all internet addresses, it contains just a portion of the web address space, when it is not able to solve the address just call another DNS making a so called recursive query.
The DNS calls a so called root server (1) to ask who hold information for the .com domain.
the
Root server answer (2) with one or more zone owner that has the needed information.
So the DNS can query directly (3) the new DNS that master that specific zone (.COM) and usually receive as an answer the addresses of the DNS servers that owns the domain interested (4).
Finally the DNS server can ask (5) to one of the owners of “myusualdomain.com” the requested page “www.”.
The DNS owner of “Myususaldomain.com” can either answer directly to the DNS server that make the request (it’s usually the case) or can give to the DNS server the address of another DNS server that own that specific address that need to be translated.
At the end, after all those iterations the DNS server can answer the client with the correct address requested.
Now the browser can finally ask to the web server the page.
The request looks somehow similar to the pic, what the browser ask it is usually an index page (index.html or index.htm) that contains the info needed to create the page on the browser.
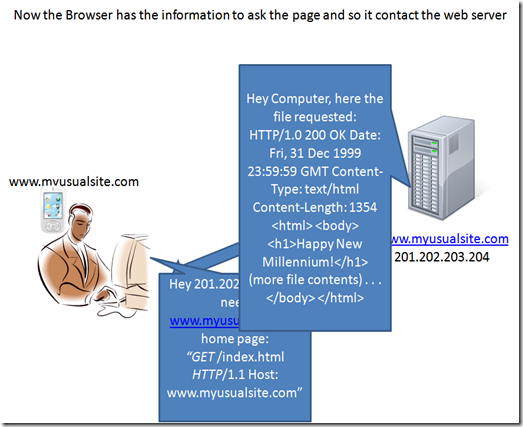
the answer , as you can see, is a file that contains a lot of indications, links and other resource references.
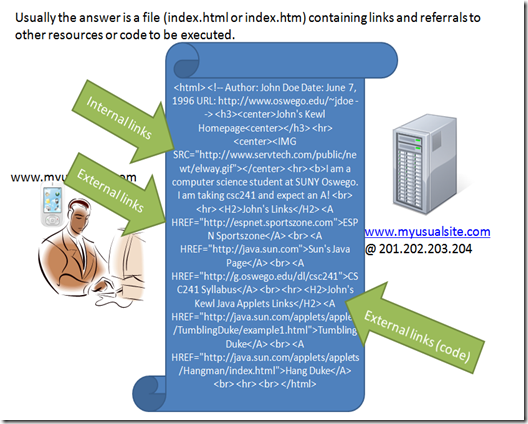
the references that are indicated inside an index file can be internal to the same webserver, external to the webserver or even code to be executed, like java or flash code.
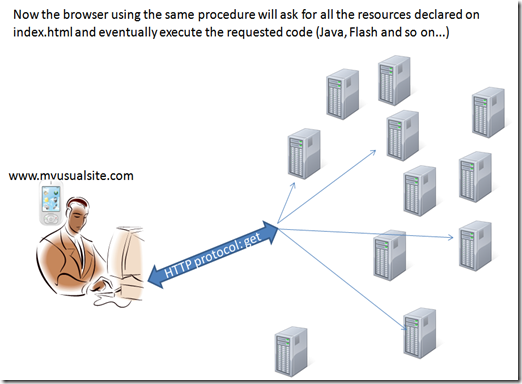
when the browser read the index code start executing the request, asking for all the resources and executing the requested code I order to compose the requested page.
The page we see into our web browser is the final result of a complex set of activities that involve several players. from the DNS resolution to the execution of code nothing is like it seems, a webpage is NOT the result of a single machine answering a request, but involves a lot of different sources.

When everything is good and all the transactions are clear browsing is an amazing activities. But in such a complex situation we can have a lot of things that can go wrong. some can be just mistakes and result in just an unsatisfactory browsing experience, but sometimes things go wrong on purpose, means someone try to use this complex process to do something bad  .
.
the main problem we can face is that when trying to download and execute everything needed to create our page something unwanted comes and reach us.
Since a page is composed by different objects and code any of those object could have been compromised.
We could point to this object directly because the source itself has been compromised:
for instance the index file, to force us pointing to a compromised resource
or the DNS can have been poisoned and direct you to a compromised resource.
either way the result is that you are directly trying to contact a resource that can be dangerous.
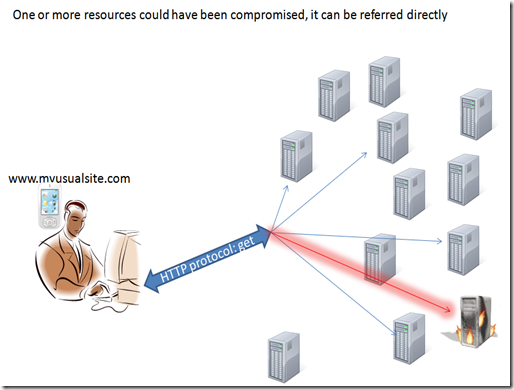
but there are also trickiest possibilities.
When we call a resource, we cannot assume the resource itself will provide all the needed output to us. the resources itself could need to call other instances and external resources. So the result is that we can have a risk of compromising not only related to The resource we directly contact, but also indirectly by a resource’s resource  .
.
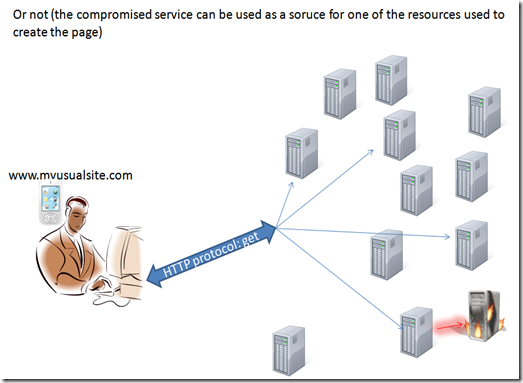
Virtually there are unnumbered possibilities to create a security outbreak in this situation.
Keep in mind that using different layers when creating a web services is related to several factors, the complexity of the output, security between layers, scalability and so on. The more complex the web become the more layers and risk of compromising we have.
E-commerce, social networks, web applications and services are just the most common example of this kind of approach.
Once a resource is compromised we face, usually different type of risks:
- The web service or page steal information redirecting, copying a standard data flux (for example an e-commerce credit card transaction) or just asking information that are not processed by the legal site.
- The web service or page try to execute code for instance to look for data or change permissions on the host platform in order to allow a later access form an intruder
- the web service or page can try to download code to be executed in the host infected machine at intruder’s will
- …
- a mix of all those issues and many many more (the sky is the limit
 )
)
all the rumors about malware recently just refers to one of this possibility, to download something in your device.
Actually it is not strictly necessary to download something, could be a permanent redirection to a service, or any other possibility. but keep it simple to understand what happen.
The infected resource become a part of the process that generate the page, thou when the user got it’s page it has a surprise attached.
the user experience can be unaffected by the compromised process, so the user usually has not idea that something went wrong.
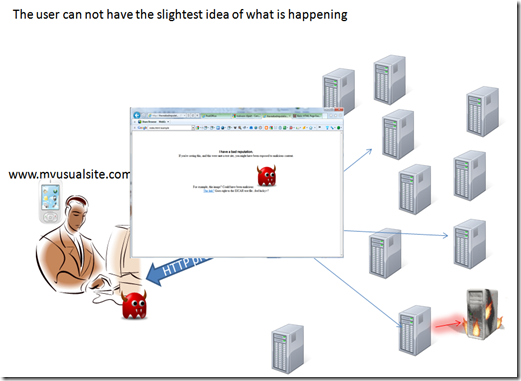
while browsing there could be background task executed without the user being aware, we should always keep in mind that a browser can perform a lot of task, like executing code, interacting with the host operating systems and many more.
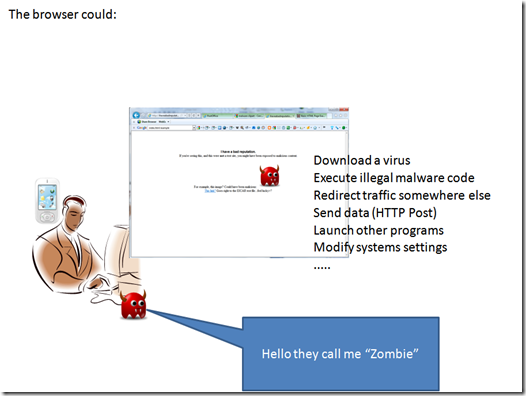
to do those kind of stuff malware writers usually compromise web services and leverage some vulnerabilities in the applications or operating systems running on the browsing device.

But why we should be worried by this scenario?
The easiest problem is data tracking and data redirection:
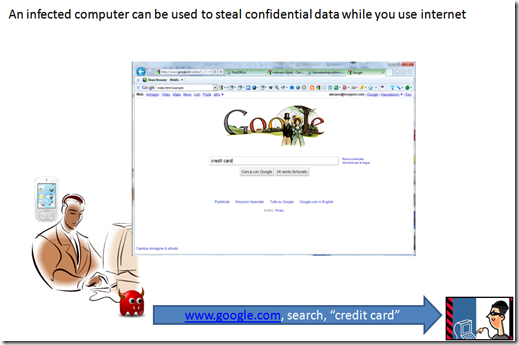
In this scenario can be several way to track or redirect data, cookies, host file compromised, plugin running with the browser and so on.
But since any browser can browse your file system and send out data with a simple “http post” a more scary possibility is that something just not copy web browsing data, but that actually look for something in your file and send it out to someone else.
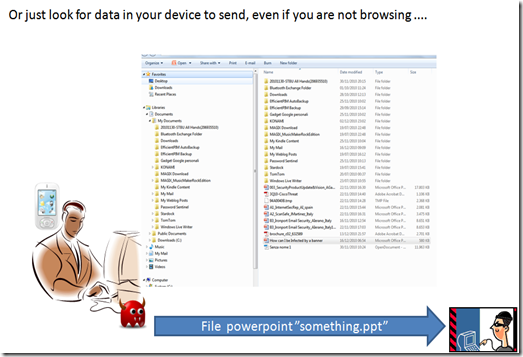
we should consider that this can be done as a background task, and does not even require the browser be opened or visible (beside we can have a browser instance running even if we don’t know about it, just using services in background without the running GUI that is just one of the components of the browser).
even more scarier is the fact that a well written piece of code can browse not only your local resource, but also remote resource using your device as a vehicle to be easily inserted in your network (making your device a sort of Trojan horse), may be using your credential and privileges to have easier access to resources.
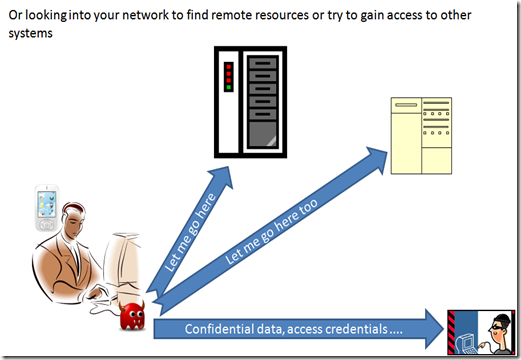
The malware itself can, this way, reach place that does not even has internet access, and same times can replicate itself to become more effective in it’s tasks.
and of course it can modify system settings in order to obtain the needed result and hide itself.
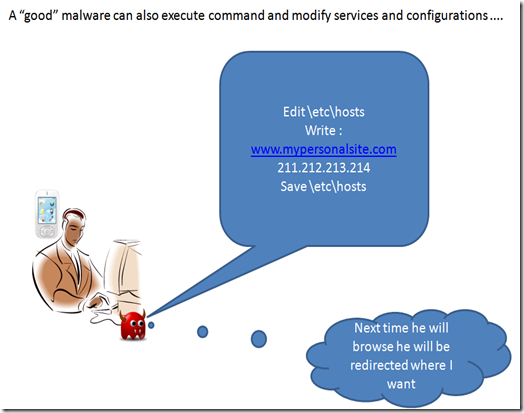
Beside data gathering a malware can also perform different tasks, the most common are sending data and requesting external services.
as an example of the first task is sending out mail using smtp protocol (usually this is the technique used to send out spam)
as an example of the second task is sending http or dns request for ddos attack.
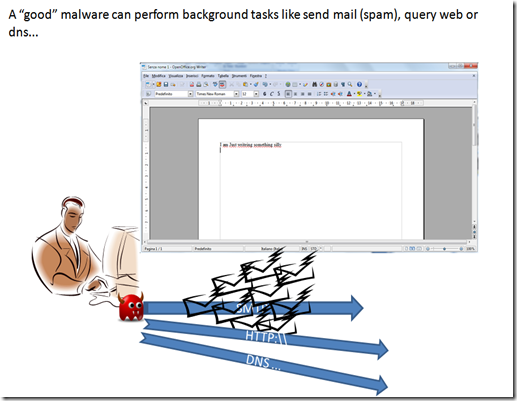
usually the modern malware is able to perform different and complex tasks, but it need instruction on what to do.
Receiving instruction require an interesting approach, since it is not possible to know where the malware will be hosted it is quite difficult to make a discovery, so most malware infected device use to announce themselves to the controlling unit.
this activity is usually called “phone home”, and the aim is to let the controlling unit to send instruction to the controlled devices.
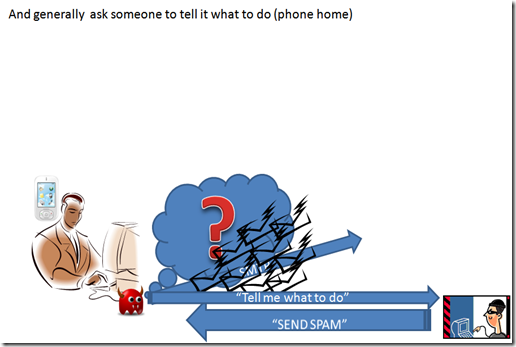
To be more effective the technology used are quite sophisticated. The discovery and communication is usually based on a mix of standard and P2P protocols, the controlling unit, or master, are usually elected inside the malware realm using sophisticated election procedure. The idea is to have a system that can provide always a master to make the infection always effective and useful (at least for the bad guy). The use of P2P technologies make the system more stable to accidental discovery of infected units making, at the same time, more difficult to find master and control units.

Due to it’s nature the infection try to hit any device possible, the more the better. Big numbers can provide better performance while remaining relatively undetectable, drowning just a few resources form the hosting device. When we are in presence of a large number of infected machine controlled by a logical master (they can be several physical devices, organized in layer to make more difficult the backtracking activity) we use to call it a “botnet” ( from “robot network”, where robot reminds to it’s literal meaning of “slave”) and the infected device “zombie” (brainless executors).
the result can be visible through the world, take as an example the rustok botnet, specialized in sending spam.
or, just making another recent example, the dos attack against Wikileaks and the “payback campaign that stroke some sites with some other dDOS attacks
one of the aspect we should consider is why they do all this.
About recent security outbreaks and issues there have been some misunderstanding. the wrong idea is that the end user is not an interesting target, while big datacenter with tons of data are.
The truth is that both the aspect are lucrative and always are related. Hitting a large surface, as botnet does, give the power to control and move great amount of data, even if the single data moved by de single computer can be relatively small.
To make my point clear I will refer to the recent wikileaks publication. if they would have published just a dozen of cable the would not been any issue, probably some mumbling but nothing more. but the number made the difference, so a little leak would not be noticed but a big one make a lot of noise. at the same time a single zombie can move detect or steal just a little amount of data, but all a botnet together can make the difference.
Botnet use can vary form sending lucrative spam, to blackmailing site, corporations or even government as recent story told us.
Even political issues can leverage cyberwar and cyber attack. beside the botnet itself could be used to make possible to break security also to reach specific target, like the the stuxnet affair teached us.
Recent site hack also showed us how classical security breach can be used to feed botnet (think of recent walgreen, mcdonald, gawker media, honda or vodaphone ones).
Recent history taught us that botnets and similar technologies can be used for a variety of scopes.
and we are just scratching the surface. there is a complex cyber underground economy working out there that move an impressive amount of money, just to understand the volume enough to be more lucrative than the illegal drug commerce.
there are some consideration that we should keep in mind: browsing the internet is something that is part of our everyday life, and is a key point in our business productivity. Through internet we exchange information and some of them are really sensitive.
Another point is related to the fact that browsing, also in an enterprise environment, is not related only to PC, but there is a great number of devices with browsing capability, and this number of devices is increasing. we can fool ourselves telling us is not our case, but we would just lie.
since this is a complex world I am afraid to say there is not a simple solution, no silver bullet. The key is to use a mix of different technologies to address the several risk that browsing expose us and our network.
alas there is a topic point, we will not able to do everything at user end side, there is no way we can give the correct level of protection working only at user device end, some technologies simply would require too much data and resource to work that way, so the protection could be done by a mix of software, network devices, endpoint software and cloud services.
so let us take a look of some technology that can help us to mitigate the issues we talked before.
one of the most effective solution in order to address browsing problems is called “reputation service”. reputation services can be implemented in several security solutions: proxy, firewall and IDS are the usual owners of this kind of technology.
the idea here is to be able to monitor internet sources and give them a “rating”. A reputation service is not a black list, is a way to express the risk we are facing when contacting a source. this risk can be high, low, medium, terrible, marginal. a reputation service is used to be an ideal companion to other techniques.
working with reputation services an antimalware and an antivirus solution can more effectively address risk coming from an apparently harmless transaction:
antimalware and reputation are here key to extend the range of protection offered by traditional antivirus techniques, since sometimes there are legit methods used to do non legit tasks. remember that the main difference between an antimalware and an antivirus is that the first is analyzing the transaction (client and server side) while the second look for bit strings inside downloaded objects.
so while an antimalware solution can stop dangerous transactions (like writing the etchosts file) an antivirus solution can stop the download of a malware piece of code in the reciving device.
but once you got infected (and sooner or later you’ll be) it’s worth to address the problem before it become a threat for your network.
One of the first sound things to do would be to avoid phone home from your infected device in order to minimize theyr activities. this can be done leveraging antibotnet technologies as in Cisco ASA. Here the aim is to stop a call form the infected device (internal) to the master (external to your network). without orders a zombie is less dangerous.
another good idea can be the use of an IPS systems. one of the biggest limitation of IPS has been always the big number of false positive, this can be addressed using reputation technologies like in cisco IPS (global correlation) or tipping point.
antibotnet systems like the ones we just mentioned (IPS with global correlation and antibotnet) can be used also to protect against dDoS attacks addressing only the call coming form botnet members and letting the good ones working.
at the same time is key to address the not correct access to internal resources. This is where Cisco Trustsec solutions could help.
the problem is, as we mentioned before, that an infected device could try to reach different resources, so it is mandatory to limit the perimeter of the data a user can reach from a network perspective to avoid data leakage and infection spread. key here is the capability to limit user traffic and not just on “IP” basis only
and, of course, beside the usual mandatory local antivirus and antimalware we should not forget a complete mobile security solution with a connection manager able to provide vpn capability posture assessment, web security with ssl tunneling and DLP, and so on.
Of course part of the deal should consider a real DLP solution (not just content filtering).
this is enough as a quick overview, any question is welcome
see you later
antonio ierano
 Image via Wikipedia
Image via Wikipedia![[Dancho_Danchev_photo_2010.jpg]](https://i0.wp.com/3.bp.blogspot.com/_wICHhTiQmrA/S3cJTbOYe5I/AAAAAAAAEgo/Ts-BIxcnoJ8/S220/Dancho_Danchev_photo_2010.jpg?w=900) eSecurity Planet
eSecurity Planet